What is VRAM?
Find out about VRAM

When getting your hands on the best graphics card on the market, its graphical performance is the most important asset as it determines the level of games it can handle. However, there's another hidden spec that's almost as important and yet not discussed nearly as much as it should be.
Before we can get into VRAM, it's vital to discuss what RAM, or random-access memory, is. RAM is essentially the memory a processor retrieves data from to perform its tasks. Since it would take too long for a PC to access data directly from a hard disk drive or solid-state drive, RAM acts as a speedier option for when your system needs to quickly move files around while running your apps and games.
This means that having a good amount of RAM is absolutely vital to a fast-running PC, as it ensures that it doesn't need to rely on swapping data to a special file in your storage devices. In other words, lots of fast RAM makes for a fast and well-running PC.
VRAM Explained
What is VRAM?
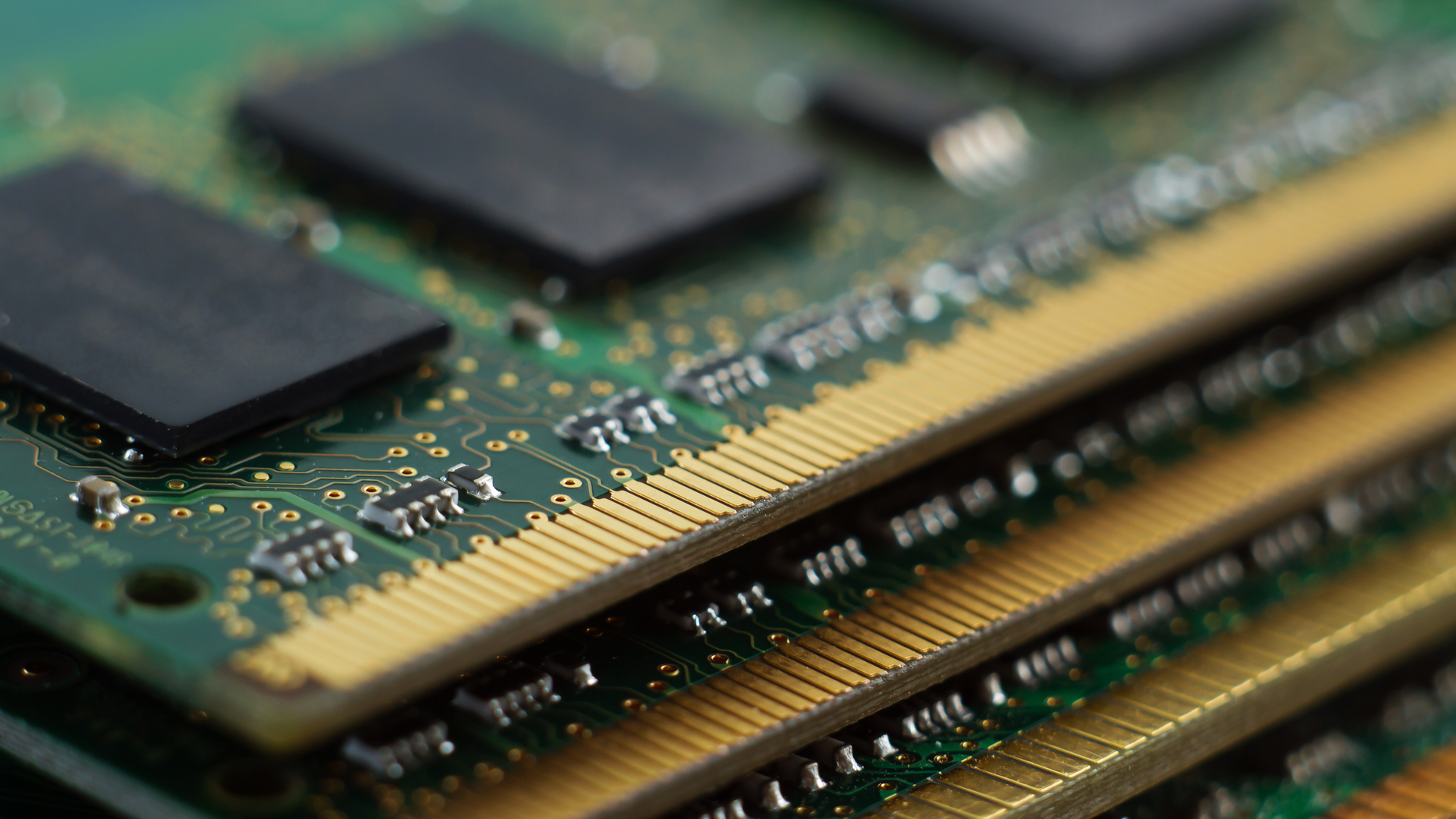
VRAM is RAM that's connected specifically to your graphics cards instead of a motherboard. It's also known as texture memory because it's temporary memory for data devoted to rendering graphics.
The data needed can vary greatly and includes stored textures, detailed meshes that wrap rendered objects, positional data that determines where objects are in relation to each other, or a variety of buffers related to things like color, lighting and shadows, and more.
Why is it important?

While VRAM has always been around, in recent years it's suddenly become much more important and discussed at length. There are quite a few reasons for these, which all come back to the rise in high-quality textures being used.
The first is higher texture resolution, as games normally store texture resolutions higher than what the actual object requires to be rendered.
The second is duplicate textures, in which VRAM stores lower-resolution textures as well as high ones, as the latter are applied to objects at greater distances. This is a process called MIPmapping which avoids the moiré effect.
The last one is ray tracing, a more recent process that creates a massive amount of data. Bounding volume hierarchies (BVHs) group together objects to better optimize ray tracing but this too uses a considerable amount of VRAM.
Types of VRAM

There are several types of VRAM, each with its own properties:
Multibank DRAM (MDRAM) is high-performance RAM that's divided into several 32KB parts. This increases performance as well as makes it cheaper than other types of VRAM.
Rambus DRAM features a proprietary bus that speeds up data flow between VRAM and the frame buffer (which contains data representing all the pixels in a complete video frame).
Synchronous Graphics RAM (SGRAM) is a clock-synchronized DRAM that's not expensive, and though it's single-ported memory it can act as dual-ported memory.
Window RAM (WRAM) is a high-performance VRAM that's dual-ported, has about 25% more bandwidth than VRAM, and costs less. It can also be used for high resolution using true color. Despite the name, it hasn't got anything to do with Microsoft Windows.
How to check for VRAM
Now that you know the importance and types of VRAM, how do you go about checking how much you have in your graphics card? There are two ways to check.
The first is by looking up your manufacturer's specs online and the second in Windows is by checking your PC's settings.
The latter is done by searching for "Advanced Display," and then clicking View advanced display info to open Advanced display settings. You can also go to Settings > Display > Advanced Display. Then click Display adapter properties, and your VRAM will be listed as Dedicated Video Memory.
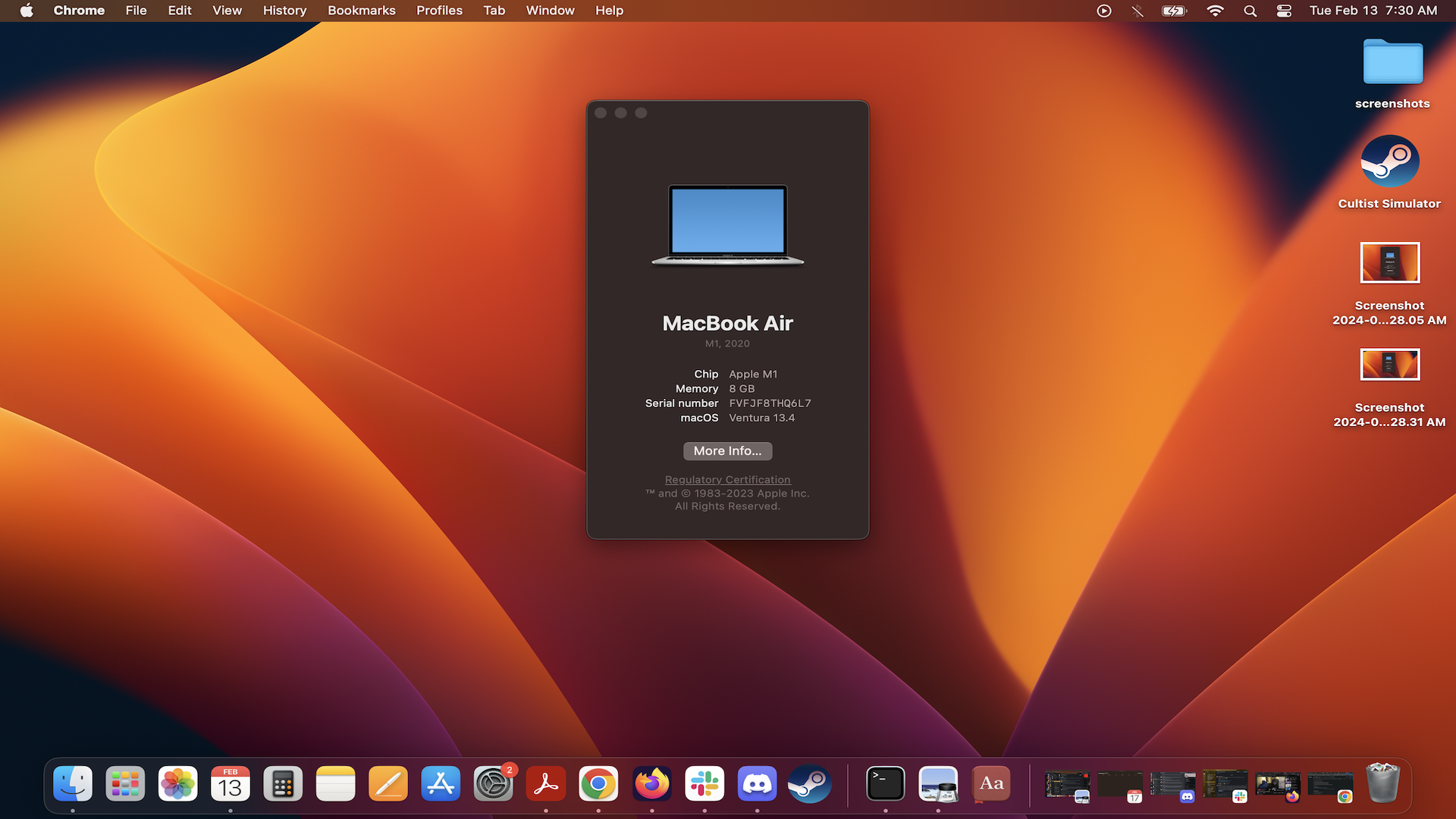
For Mac users, click the Apple icon, then go to About This Mac, and your VRAM will be listed next to the graphics processor's name.
It's worth bearing in mind that modern Mac products (those using Apple M1 or newer chips) have 'unified memory' instead of dedicated VRAM, which means the existing system RAM is shared between the CPU and GPU. As such, you might not be able to view the total VRAM if you have a more recent macOS device.
How to maximize VRAM
The most obvious way to maximize your VRAM is by buying a graphics card that has the amount of VRAM you desire. The bare minimum you'll want for gaming purposes is 4GB, but much of modern gaming demands at least 8GB to be speedy enough.
You can also adjust your PC's settings to maximize VRAM. The first place to start is with textures like texture, texture detail, or texture resolution setting depending on the game. Ray tracing can also be adjusted or even turned off with very impact on your game, while significantly decreasing the VRAM usage.
If you're on a macOS device, there's not much you can do to improve your VRAM (short of buying a new product) since the best MacBooks and Macs have unified memory that usually can't be user-upgraded.
Final thoughts
VRAM has always been important to gaming performance but in recent years we've seen an uptick in how much it's been emphasized, as well as how much is considered standard.
Several years ago you could comfortably suggest 2GB or 4GB as long as your gaming wasn't strenuous. But most of the best PC games now require a bare minimum of 4GB, with 8GB being the much more suggested standard and 16GB considered to be what most gamers would recommend to prevent slowdown and stuttering of any kind.
It's interesting to see what's become the new standard in VRAM, though it could also be seen as detrimental to PC gaming considering that more and more games are requiring a spike in VRAM. Hopefully, games in the future can become more efficient in VRAM usage to prevent the requirements from climbing too high.
You might also like
- Nvidia RTX 4080 Super could fix one of the biggest complaints
- The best graphics card in: top GPUs for all budgets
- What is a graphics card: All about this important PC component
Get daily insight, inspiration and deals in your inbox
Sign up for breaking news, reviews, opinion, top tech deals, and more.

Named by the CTA as a CES 2023 Media Trailblazer, Allisa is a Computing Staff Writer who covers breaking news and rumors in the computing industry, as well as reviews, hands-on previews, featured articles, and the latest deals and trends. In her spare time you can find her chatting it up on her two podcasts, Megaten Marathon and Combo Chain, as well as playing any JRPGs she can get her hands on.