How to port forward for faster internet speeds
How to port forward and boost your connection

In this guide we'll show you how to port forward using your router. Routers are becoming easier to set up, and if you're into sharing files over the internet and using P2P networks then you'll need to know how to port forward on your router for the best results.
Port forwarding – sometimes referred to as tunnelling – involves opening a network port from one network node to another. This technique enables another user to reach a port on your router.
Software ports are numbered connections that a computer uses to sort types of network traffic. A port may support incoming traffic, outgoing traffic or both.
A few services, such as FTP (on port 21) and HTTP (on port 80), are assigned by default to open ports where operating systems can find them easily.
When a port is opened a service is assigned to it – for example, an online game or P2P client. For security reasons, all ports to the internet and most LAN ports are closed by default so that traffic can't flow through them.
The actual process of port forwarding is complicated and involves a combination of routing by port combined with data packet rewriting – but don't worry, as that's where our guide to how to port forward comes in.
A conventional router examines the data packet and dispatches the packet depending on the packet's destination address. Port forwarding examines the packet header and forwards it on to another host, again depending on the destination port.
Get daily insight, inspiration and deals in your inbox
Sign up for breaking news, reviews, opinion, top tech deals, and more.
Forward thinking
You forward ports in your router's admin panel, but the actual process varies according to manufacturer. Look for 'Rules' or 'Application' settings. The 'Rules' area of your admin panel is where you can maintain a list of applications to allow or block.
In the first box you'll usually enter the name of the application that this will apply to. You'll then need to enter a start and end port (port range) for the application to direct its traffic through.
First check out this excellent guide covering hundreds of common applications and games. Click 'Enable' or 'Allow' on your chosen port.
You may need to restart your router for settings to take effect.
1. Find your settings to port forward
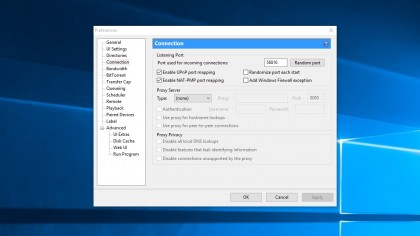
For a file-sharing client such as BitTorrent you need to find out a few settings before entering the rules into the router admin panel.
Go to Settings > Network and note the start port that's being used. .
2. Router admin panel
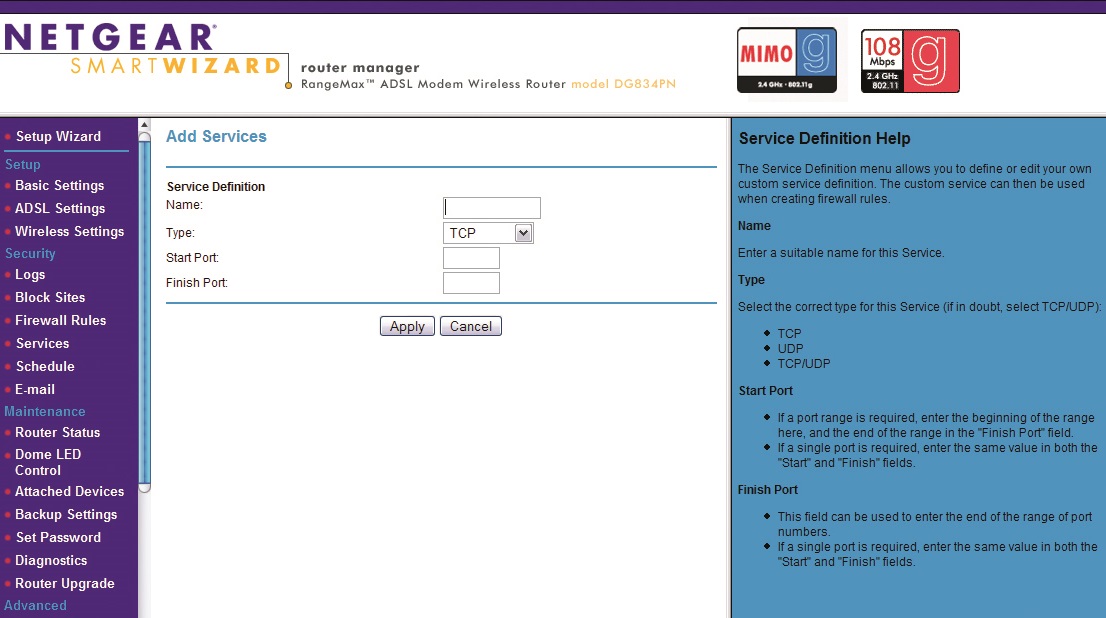
Armed with a static IP you can now begin the process of forwarding the ports through your router's admin panel. To access the router admin panel you need to open up your internet browser and enter in the IP address of your router.
This is usually something like 192.168.1.1, but it can vary depending on your router so check the manual or search online if that address isn't correct.
Next, log in and look for the Rules or Applications area. Click 'Add' or 'Create Rule' (depending on your router).
We have a special Netgear router login guide for how to log in and tweak your settings.
3. Configure the firewall
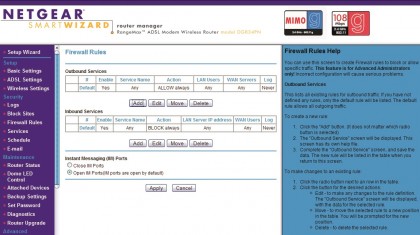
With the port ranges entered you now need to make your router's firewall let the traffic though that port. Under Firewall Rules (or equivalent) click 'Add' and then name your service (uTorrent, for example).
4. Enter the static IP
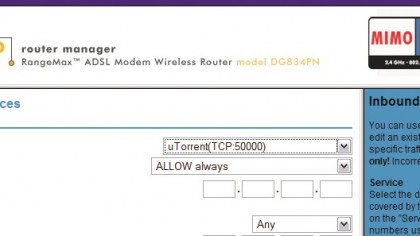
You'll need to enter the static IP. Then select an action – this can vary from Allow Always to Block Always and commonly includes options to schedule when the port is open.
Again, it depends on your router.
5. Configure WAN settings
You may also have fields for WAN (Wide Area Network) settings. These are the settings used to connect your ISP.
These will be the Name Servers or Primary and Secondary DNS settings you found for your static IP.
6. Check your router settings

All routers are different and the tutorial here might not have everything your router requires. Take a look at this great port forwarding resource for common ports and what specific routers require from you.
- Best PC games 2019: the must-play titles you don’t want to miss