How to use Gmail
Learn the basics
How to use Gmail
Gmail is, in many ways, the core service in Google's suite of office tools. It connects directly with Google Calendar and Google Plus.
Gmail attachments are opened in Google Docs or can be saved directly to Google Drive. Tasks, now a feature of Calendar, originated here – as did the practice of using labels instead of folders, which is widely implemented across Google apps.
On top of this, of course, your Gmail account is how you connect to all the other Google apps. It's your Gmail address you use to log into Docs, Plus, YouTube and all the rest.
Big numbers
The last time Google published figures, it announced that Gmail had around 425 million active users, and an educated guess would put the figure closer to 600 million now.
That's a larger user-base than both Microsoft's Outlook Live service (formerly Hotmail, which had a massive head start over Gmail) and Yahoo! – its closest rivals.
There's a good reason for this. Gmail offers a sophisticated mail service with a lot of features you used to get only in desktop software. It's reliable, offers lots of free storage and it sorts your mail for you on the fly.
Plus, Gmail's smart spamfiltering has made junk mail something we can almost forget about. Here we'll take a look at some of Gmail's basic and not-so-basic features, so that you can get the most from the world's most popular email service – which, of course, is also free.
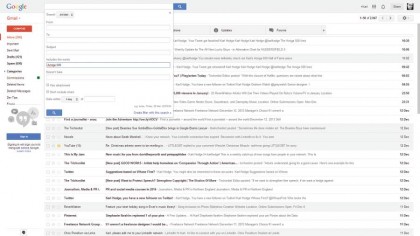
1. Fill your inbox
With Gmail you never have to delete a message. It gives you 15GB of free storage (shared with Docs and Google Plus) and a powerful search tool so that you can find any email ever received or sent.
A quick tip: click the small arrow at the end of the search box for advanced search options.
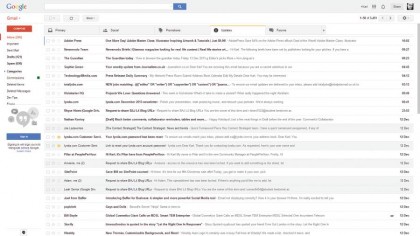
2. Automatic tabs
By default, Gmail sorts your mail into tabs for you. Primary is for person-to-person messages, Social for updates from Facebook and the like.
Promotions is for advertising mail you've opted into; Updates are auto messages from services you use; Forums are messages from mail groups.
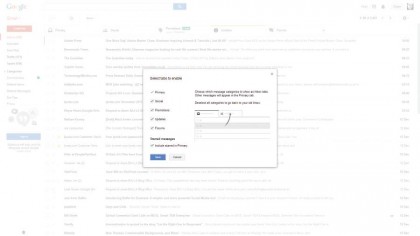
3. Configure tabs
To configure tabs, click the + icon at the end of the tab bar to view a list of tabs that you can switch on or off.
Removing a tab doesn't remove the mail – it will get distributed into other tabs. Finally, tick "Include starred in Primary" to quickly move starred mail to your main tab.
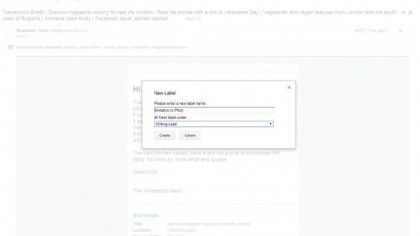
4. Creating labels
Gmail doesn't have user folders – but it does have Labels to help you organise your mail. To create a Label, open the message you want to categorise and click the Labels icon.
Choose Create new label. Labels can be nested like folders, so can have sub-labels within a category.
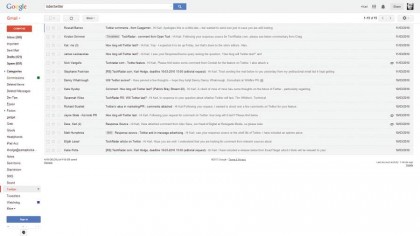
5. Using Labels
When you've created a Label, it's easy to use it. In any Inbox tab, select one or more emails by ticking the box next to the sender info. Click the Labels icon and choose a Label from the list. To see emails that are organised with a label, select the label name from the sidebar.
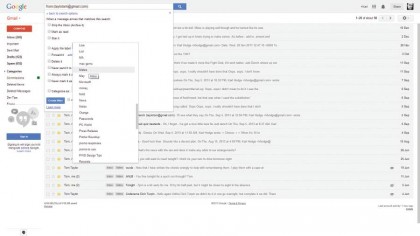
6. Filters
You can get even more from labels – use them to tag incoming mail automatically. Click the arrow at the right of the search box and enter a search term.
Click "Create filter with this search". In the next dialogue is a range of things Gmail can automatically do to emails, including add a label.
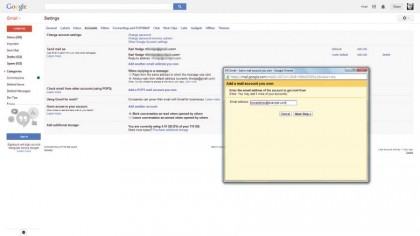
7. Add POP email
Gmail can retrieve mail for you from other email accounts. Click the Settings icon and choose Settings. Click on the Accounts tab and choose "Add a POP3 Account you own".
Enter the email address of your other account and click Next. Gmail will fill in the details – you provide the password.
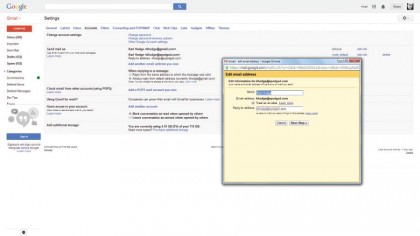
8. Use your own address
If you own a domain name with an email address, you can use that with Gmail. First, you should set up the domain so that it forwards mail to your Gmail address – check with your domain name provider.
Then in Gmail go to Settings > Accounts and choose "Add another email address you own".
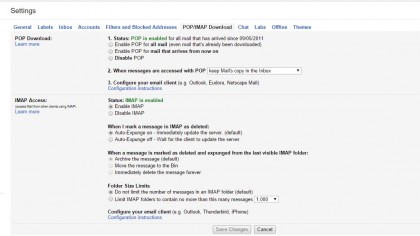
9. Use Gmail with Outlook, Thunderbird and more
To access Gmail from other mail apps such as Outlook, you'll need to enable POP and IMAP.
Go to the "POP/IMAP Download" tab in Settings and click the Enable buttons for both of these.
In the email program you want to use will need to enter in your email address and the following information:
Incoming Mail (IMAP) Server:
- imap.gmail.com
- Port: 993
- Requires SSL: Yes
Incoming Mail (POP3) Server:
- pop.gmail.com
- Port: 995
- Requires SSL: Yes
Outgoing Mail (SMTP) Server:
- smtp.gmail.com
- Port: 465 or 587
- Requires SSL: Yes
- Requires authentication: Yes
- Use same settings as incoming mail server