
1. You’re too far from your Wi-Fi router
One simple reason why your internet may not be working as well as it should be is that you’re not in a great spot to pick up a Wi-Fi signal.
If you’re far from the Wi-Fi router or have many walls, floors and lots of objects between your device and the router, you’ll probably have a poor connection that can slow down your internet access. Stone, brick and concrete walls will especially interfere with your signal, as can any device giving off its own wireless signal, like a smart home device.
If you can carry your device somewhere else, this is an easy fix.
2. A poorly-located router
Where you are with your phone, tablet or computer is only half the battle. If you’ve put your Wi-Fi router in a bad location, you may get slow internet and unstable connections on all your devices.
Ideally, your router will be placed somewhere central, so its signal can reach across the house or apartment. But it should also not be placed right next to other electronics or metal objects that can interfere with its signal, significantly slowing down your internet surfing.
3. Crowded network
If you’re not the only person using your network, you’ll be sharing bandwidth. The pipeline between your devices and the internet is limited, and if a lot of devices try to send and receive a lot of data, they’ll have to take turns. This will slow down the internet for everyone connected.
For Wi-Fi networks, numerous connected devices can also lead to a slow down, as the Wi-Fi communicates with each device in turn. This is especially true with a Wi-Fi router that supports fewer bands (more on this later), as more devices will be sharing the same resources.
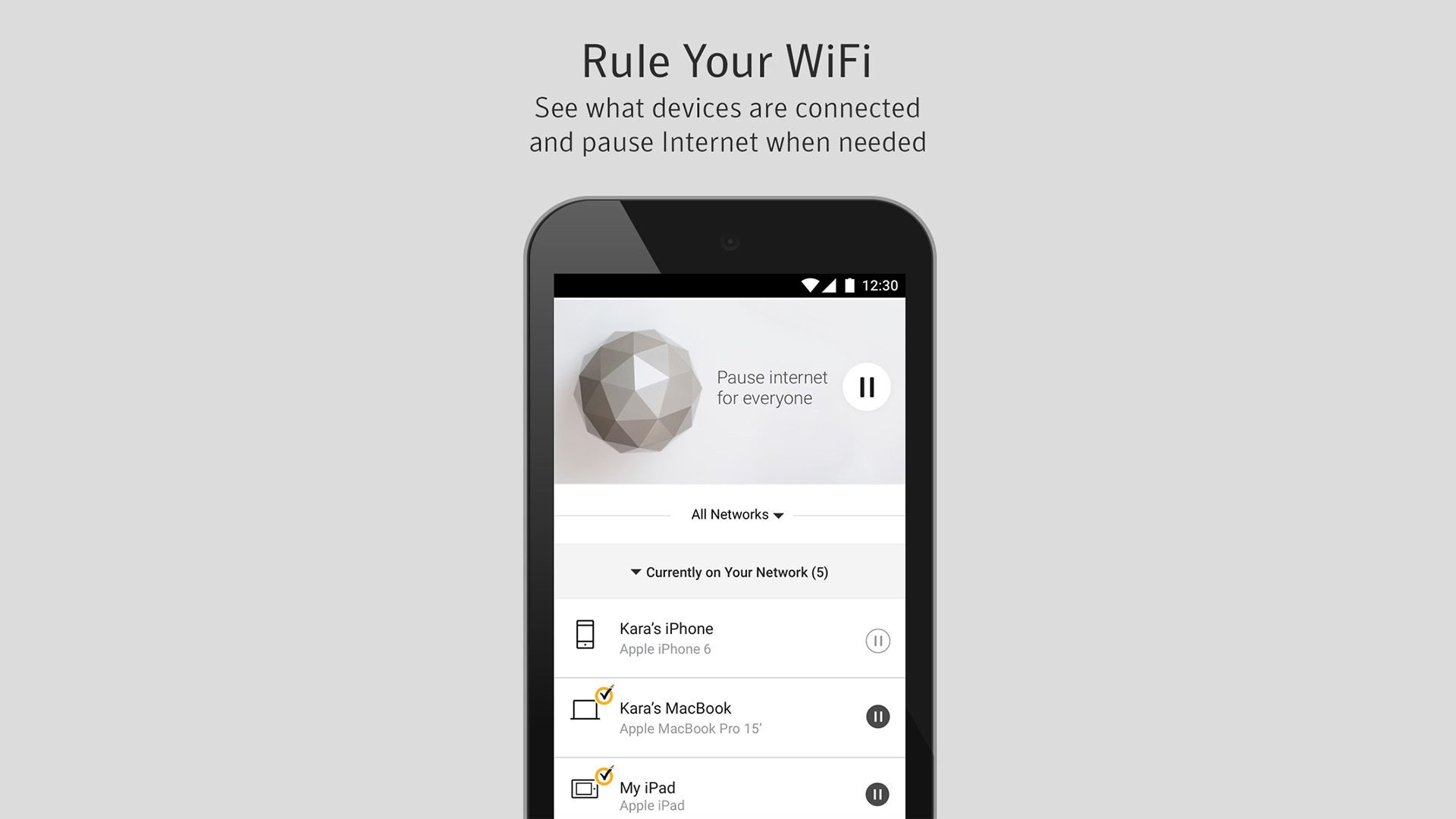
4. Unsecure network (which can lead to #3)
One of the greatest sins you can commit when setting up a Wi-Fi router is to make a public network, which anyone can connect to without a password. Even adding a separate guest network could result in some of your bandwidth getting used by strangers. And don’t think it’s much more secure if you add a simple password that someone could easily crack.
Aside from putting your information at risk by not protecting your network and allowing potentially unknown users to access your network, you could be sharing your internet connection with users who will enjoy free internet while cutting into your bandwidth. You don’t want to let your Game of Thrones stream slow down because your neighbors are also streaming Game of Thrones on your Wi-Fi network.
A secure Wi-Fi router like Norton Core can help keep your network secure, monitoring for unauthorized access, prompting you to secure the network with a strong password, and even issuing temporary guest passes, so you don’t accidentally leave the door open for unwelcome guests on the network later on. Norton Core also allows you to see what devices are using your home network and block or pause those devices’ connections. This makes your network safer and ensures your internet isn’t slowed down because a passing stranger stopped to hop onto your network and download a movie or two. Norton Core can even prioritize individual devices, so you can be sure your internet browsing isn’t slowed down by others on your home network.
5. Competing Wi-Fi signals
It’s not just your neighbors using your Wi-Fi that you have to worry about. They might have their own Wi-Fi networks that could interfere with your own and result in slow internet. This scenario is more likely in apartment buildings, where many people are living close together.
The overlapping signals coming from multiple Wi-Fi networks will interfere with one another. While newer Wi-Fi routers will support 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequencies, many older routers still in use only support 2.4GHz, and that can lead to interfering signals, thus slowing down your internet connection.
One way to potentially resolve this is to use a free Wi-Fi analyzer and see which bands (small sections of the 2.4GHz frequency) are being used by nearby Wi-Fi networks. If you see nearby networks are using the same band, and that another band isn’t being used, or has some weaker networks on it, you may be able to switch the band on your router to reduce the interference with nearby networks.
6. It’s just not as fast as other networks you’re used to
It’s possible that you’ve gotten used to faster internet in one place, and you’re not getting it in another. A cafe I frequent has such fast internet that I’d go there if I needed to download any big files. If you’re used to a fancy cafe, office or co-working space that makes great internet a priority, you might feel like your home network is slow in comparison.
This could be because you have a Wi-Fi router with limited speeds (more on this later), or because the internet service you’re paying for is not as fast as what you’re getting elsewhere. Some internet service providers offer connections with incredibly limited bandwidth, so if you’re paying for a 3Mbps connection, don’t be surprised if your internet isn’t zippy, especially if multiple users are sharing that connection.
7. Your device has limited Wi-Fi speeds
Let’s say you just got your paycheck and felt like enjoying the finer things in life, so you pulled the trigger and upgraded to your Internet Service Provider’s (ISP) Gigabit internet connection. Great, you’ve eliminated your internet service as a bottleneck, but there are still other things that could be slowing down your connection.
Not all Wi-Fi is created equal, and an old router might be using a Wi-Fi standard that isn’t going to deliver anything close to Gigabit speeds. The devices you’re accessing the internet with also can have limited bandwidth. Check your computer, phone, or tablet and the router you’re connecting with to see what wireless protocol they use (likely to be “Wireless” or “802.11” followed by some letters) and then check the check the speeds here. Then, understand that you’re not going to get internet any faster than the slowest link in the chain.
Another aspect of your router is the number of bands it offers. Since multiple devices can try to talk to the Wi-Fi router at once, extra bands can help them all communicate quicker. Say you have six devices on your network. If all six are on the same band, all six have to wait on one another as they each take their turn communicating with the router, slowing down the internet for all of them. If you have a dual-band router, some devices may be able to connect to the other band, so you could have four devices on one band and two on the other, reducing the time each device has to wait to talk to the router.
8. Local congestion or ISP throttling
Another reason you might be getting slow internet, and one that’s not easy to do anything about, is simply that there are tons of people using up the bandwidth available to your neighborhood. The area you live in doesn’t have an unlimited pipeline to the internet, and if a huge population is all on the internet at once, the congestion can slow down the internet.
This probably won’t happen often, but when it does, you’re going to hate it. When everyone in town is trying to stream the season finale of Game of Thrones at the same time, don’t be surprised if you get a pixelated Jon Snow, or even no Jon Snow at all.
You’re a bit more likely to see your internet speeds slow down if your ISP is one that uses throttling on its heaviest users. Some ISPs have bandwidth caps, and if your data usage exceeds that cap, you might get throttled internet speeds for the remainder of the month as the ISP tries to ensure other users in your area don’t see reduced speeds.
9. Background processes are hogging your bandwidth
It might not even be your neighbors that are stealing the bandwidth available to you. Let’s face it, our computer and electronic devices do a lot of stuff behind the scenes that we don’t even realize is going on. Sometimes, that can be hefty downloads that cut into your Netflix streaming speeds.
Devices that have automatic updates are likely culprits, such as a computer trying to keep its operating system up to date. If you’re browsing the internet while that update quietly downloads in the backgrounds, your browsing may be slower than usual. You can use the Task Manager in Windows or the Activity Monitor in Mac OS to monitor what programs are using your network and try pinpointing the source of the slowdown.
If you think a different device on your network is the culprit running network-intensive background processes, a network monitoring app like Norton Core can help you spot which devices are using the most bandwidth and adjust to prioritize their bandwidth.
Another possibility is a more nefarious program. Malware is a threat in a lot of ways, and it has the potential to slow down your internet browsing, especially if it’s using your bandwidth to upload files from your computer. If you can’t pinpoint what’s slowing your internet down, you may want to run a malware scan, or find a router like Norton Core that can monitor your network usage and security.
10. Your webpages are loading too many things
You might love saving yourself a few clicks here and there, but if you let sites like Facebook and Twitter automatically play GIFs and videos when you scroll past them, you’re going to tax your internet bandwidth. While fast internet with a reliable connection should be able to handle loading the occasional video or GIF, these same bites of media could make your experience much slower if you combine that with any of the other issues above.
On top of this content cutting into your bandwidth, it can also use up your devices RAM. If you use up most of your RAM, your internet will definitely start to feel slow. Why? Because your whole device is going to get slowed down.
Sponsored by Symantec
Get daily insight, inspiration and deals in your inbox
Sign up for breaking news, reviews, opinion, top tech deals, and more.