
This article is in association with Dabs.com
It seems like PCs can never have enough 3D graphics power. Higher resolutions, more effects, better image quality and film-like post-processing effects seem to keep even the latest cards working hard.
But even upgrading to a modest new card is going to offer much improved speed and, more importantly, access to new DirectX 11 effects that older cards can only dream of.
If the range of PC graphics cards leaves you a little bewildered then worry not, first have a good read of our in-depth buying guide and then have a read of our latest graphics cards reviews so you're fully armed with the best buying-advice.
Importantly with high-end and even mid-range cards it's important to check your PC's power supply (PSU) meets the minimum power requirements. Modern graphics cards are power hungry, high-end models will need a 600W PSU, while mid-range cards will usually require at least a 450W PSU.
It's important to check the specification requirements before buying. The PSU inside your PC will have a sticker on its side stating what its maximum output wattage is.
As always before opening your PC always power it down and disconnect it from the mains power supply and take anti-static precautions. Right, let's get on with the tutorial!
Get daily insight, inspiration and deals in your inbox
Sign up for breaking news, reviews, opinion, top tech deals, and more.
1. Locate your old graphics card

You'll be either installing a card into a brand-new PC or else replacing an existing older card. For the latter option your first job is to locate the old card, they're usually hard to miss, usually being the largest card inside your PC that's closest to the processor heatsink and of course attached to the monitor.
2. Remove everything

Disconnect the monitor cable and undo the backplate case screw. Then stop. Almost all motherboards use some type of physical securing system to prevent the card falling out of its slot. This could be a plastic latch, a spring-loaded pull-out button or sometimes it's just a catch. These can be somewhat hard to see, but gently try to remove the card and feel for a catch at the end of the PCIe slot.
3. Types of card and slots
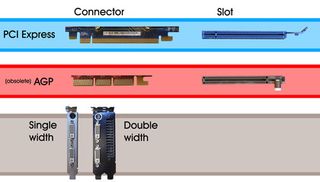
Modern cards use the PCI Express aka PCIe interface slot. The older and now obsolete slot is called AGP but was replaced by PCI Express around 2004. So if your PC was bought in the last five years, it's likely to be PCIE. Cards come in various lengths and in two widths: low-end up to mid-range cards are the standard single-width, while high-end models are double this width occupying two backplate slots.
4. Power connectors
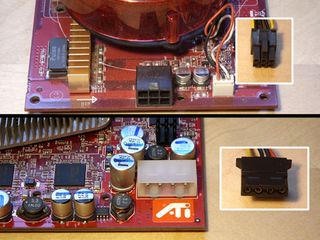
Modern graphics card can require a great deal of power to work. From mid-range upwards you will find graphic cards require additional power connectors, which your power supply may or may not offer. Older models just used the standard 4-pin Molex connector. This has been replaced by the 6-pin and more recently 8-pin PCIe power connectors. For PSUs that lacks these, your graphics card should come supplied with standard Molex adaptors.
5. Slot it in

Don't force the card, line the connector up with its slot and gently push. Often the bottom edges of the backplate can catch and need a prod for them to drop into place. If your motherboard has more than one large x16 PCIe slot, use the one closest to the processor. Depending on the type of latch on the slot, this may also need you to unhook it before the card will lock into place, but they're designed to automatically snap in.
6. Connect up

Replace the backplate screws to secure the card in place. If you haven't already connected any required power adaptors then connect these to the graphics card. If the card has more than one, they will all need connecting to the power supply with a suitable adaptor.
7. Video output

PCs have a confusing number of video output: VGA (d-sub), DVI, HDMI, DisplayPort and that's beside older TV-out options such as S-video, composite and component. The most common is the large DVI connector and most graphics cards will provide two of these, plus adaptors so you can connect older VGA displays. It's also possible to use adaptors to connect HDMI and DisplayPort to DVI connectors.
8. Driver installation
Depending on the OS you're running you may find your new graphics card working after a reboot. However it's advisable to get the latest drivers as these contain bug fixes and speed enhancements for the latest games. VisitNvidia's site for GeForce cards, while go here for ATI Radeon cards.
--------------------------------------------------------
Sponsored link: Speed up your PC's graphics with a latest-generation DirectX 11 card from AMD - the Radeon 6850 is available from Dabs.com from less than £150.
--------------------------------------------------------
The TechRadar hive mind. The Megazord. The Voltron. When our powers combine, we become 'TECHRADAR STAFF'. You'll usually see this author name when the entire team has collaborated on a project or an article, whether that's a run-down ranking of our favorite Marvel films, or a round-up of all the coolest things we've collectively seen at annual tech shows like CES and MWC. We are one.
Most Popular



