Internet censorship body swings into action
Japanese group charged with policing sites that could cause harm

Tighter regulation of online expression has moved a step closer with the announcement in Japan that a website watchdog will start filtering out 'harmful' sites there later this month.
The Content Evaluation and Monitoring Association (CEMA) is a private body that is working within the framework of a new law governing websites the government deems likely to provoke crimes or promote suicide, among other issues.
Protecting kids
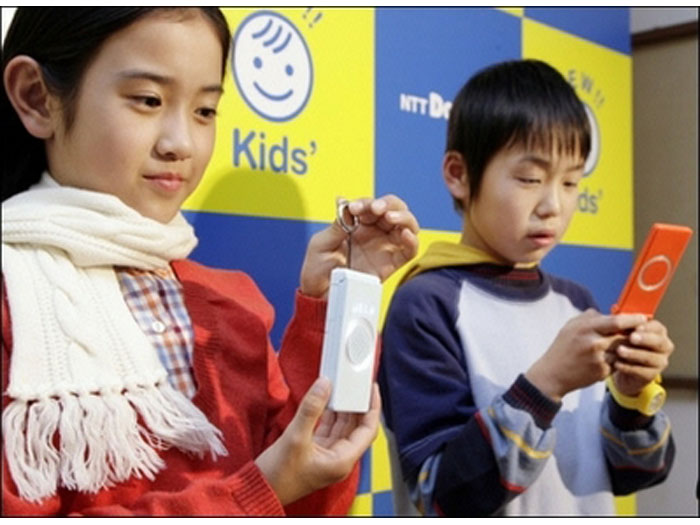
As we've previously seen, most people accessing the web in Japan do so from phones, which is why CEMA's eye will initially be on mobile sites, not sites designed for PC browsers.
The CEMA's first role will be patrolling websites aimed at children and certifying those that meet its list of 22 guidelines. Successful sites will be allowed to pass through child filters already installed on some handsets, particularly phones designed for kids.
Keeping tabs
The guidelines recommend that sites check users' ages and react immediately to threats posted online, such as those made before the Akihabara killings last month. Only the sites that keep records of phones connecting to them will be recommended for approval by the guidelines.
Get daily insight, inspiration and deals in your inbox
Sign up for breaking news, reviews, opinion, top tech deals, and more.
Websites that are not approved end up on a blacklist that – in theory – will be inaccessible to anyone under 18 years of age with a mobile phone.
As well as requiring phone companies to offer child filters, the new law also outlines plans to force PC makers to do the same, although this isn't addressed in the current CEMA plans.
Best-laid plans...
Nevertheless, the scheme isn't without its flaws. We conducted a quick poll among a group of a dozen 13- and 14-year-olds in Tokyo today and discovered that not one had a phone with filtering software.
One explained, "I'm not going to use a child's phone – they don't look cool, so I have this normal phone on my dad's account."
Although such a reaction is to be expected, one striking observation was that there wasn't a single kid who didn't have a phone. That too would not be cool. Clearly, CEMA has plenty of work ahead of it.
J Mark Lytle was an International Editor for TechRadar, based out of Tokyo, who now works as a Script Editor, Consultant at NHK, the Japan Broadcasting Corporation. Writer, multi-platform journalist, all-round editorial and PR consultant with many years' experience as a professional writer, their bylines include CNN, Snap Media and IDG.