Is this the biggest password leak ever uncovered? Researchers claim nearly 10 billion credentials under threat — here's what we know so far
RockYou2024 leak contains nearly 10 billion credentials

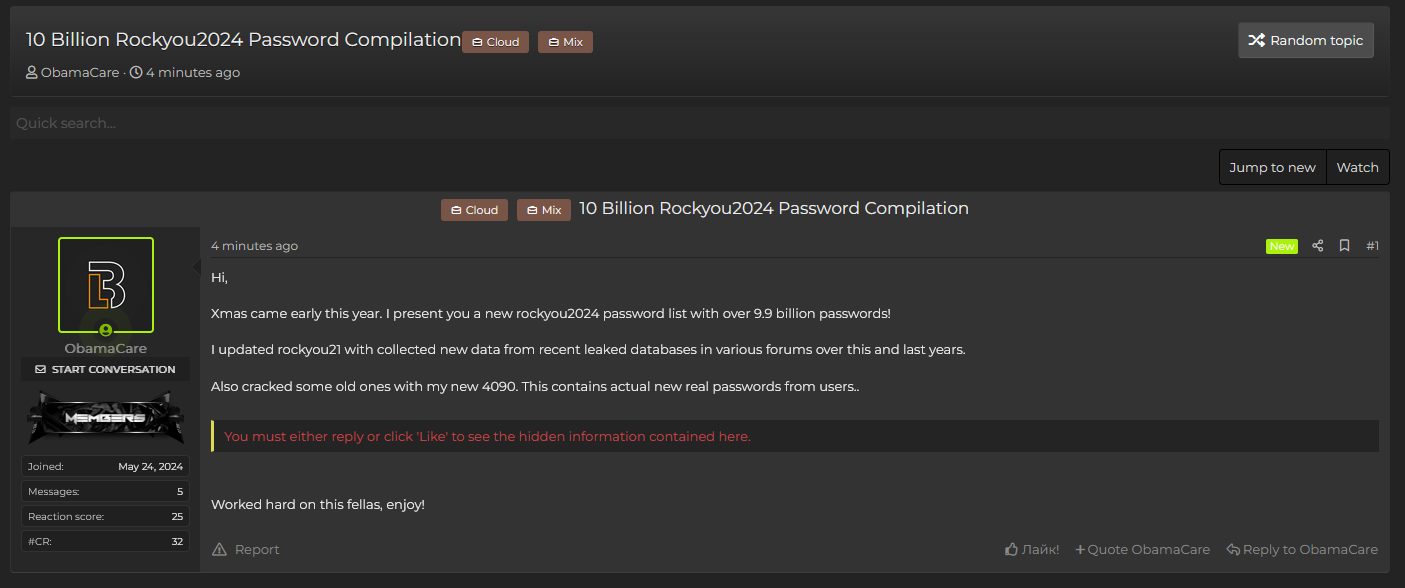
Researchers claim to have uncovered what appears to be the biggest password cache ever uncovered, with 9,948,575,739 unique plaintext passwords inside.
The file, titled ‘rockyou2024.txt’ contains passwords stolen in a mix of old and new attacks, making the file a brute force attackers’ dream.
“In its essence, the RockYou2024 leak is a compilation of real-world passwords used by individuals all over the world. Revealing that many passwords for threat actors substantially heightens the risk of credential stuffing attacks,” Cybernews researchers say.
Reader Offer: Save up to 70% on Aura identity theft protection
TechRadar editors praise Aura's upfront pricing and simplicity. Aura also includes a password manager, VPN, and antivirus to make its security solution an even more compelling deal.
Preferred partner (What does this mean?)
Brute forcing and credential stuffing treasure trove
The .txt file was posted on July 4 by a user with the handle 'ObamaCare', who has shared leaked passwords from a number of sources since registering in May 2024.
Speaking on the potential dangers of the password leak, the research team said, “Threat actors could exploit the RockYou2024 password compilation to conduct brute-force attacks and gain unauthorized access to various online accounts used by individuals who employ passwords included in the dataset.”
The passwords are compiled from a number of data breaches spanning two decades, with 1.5 billion passwords added to the file from 2021 to 2024.
Brute forcing is an attacking technique used by hackers to breach accounts by using combinations of usernames and passwords until successful entry is gained. By automating the process, an attacker can try potentially millions of passwords with ease. A system unprotected against brute-force attacks could quickly succumb to an attacker using this password database.
Are you a pro? Subscribe to our newsletter
Sign up to the TechRadar Pro newsletter to get all the top news, opinion, features and guidance your business needs to succeed!
Similarly to this, the file could also be especially useful for an attacker using a technique called credential stuffing. Using a database of stolen passwords, particularly those stolen from the target organization, an attacker would have a much higher chance of success in breaching a user account. Both online and offline services are at risk, as well as internet facing cameras and industrial hardware, the report says.
“Moreover, combined with other leaked databases on hacker forums and marketplaces, which, for example, contain user email addresses and other credentials, RockYou2024 can contribute to a cascade of data breaches, financial frauds, and identity thefts,” the research team added.
In order to protect yourself or your organization from a potential attack using this 10 billion strong credential file, the researchers recommend implementing mitigation strategies and checking credentials against the Leaked Password Checker. It may also be worth checking out the best identity theft protection.
More from TechRadar Pro
- Here is our guide to the best malware removal tools around today
- How to safeguard your network against the surge of digital assaults
- These are the best password managers right now

Benedict has been writing about security issues for over 7 years, first focusing on geopolitics and international relations while at the University of Buckingham. During this time he studied BA Politics with Journalism, for which he received a second-class honours (upper division), then continuing his studies at a postgraduate level, achieving a distinction in MA Security, Intelligence and Diplomacy. Upon joining TechRadar Pro as a Staff Writer, Benedict transitioned his focus towards cybersecurity, exploring state-sponsored threat actors, malware, social engineering, and national security. Benedict is also an expert on B2B security products, including firewalls, antivirus, endpoint security, and password management.
