Millions of voter documents leaked online — fears of election interference rise following breach
Identity theft and election interference could be tip of the iceberg

The voter documents of 4.6 million Americans have been leaked online after being stolen from 13 non-password protected databases.
The information contained within the databases included voter records, ballots, and election-related records that include personally identifiable information (PII), social security numbers (SSN), drivers license and voter ID numbers.
There are fears the information could be used maliciously to commit identity theft, data theft, voter fraud and intimidation, and even election disruption.
Elections at risk
The databases were found by cybersecurity researcher Jeremiah Fowler, and subsequently reported to VpnMentor. Fowler used news articles and freedom of information requests to identify a company called Platinum Technology Resource was responsible for the unprotected databases.
Fowler originally discovered a singular unprotected database containing information from a single county in Illinois, but upon replacing the county name within the database name format, Fowler discovered an additional 13 open databases, alongside 15 that were not publicly accessible.
Platinum Technology Resource is a company that provides election related services such as ballot printing and voter registration software, with the voter information portal linked to the exposed databases redirecting to a domain indicating “Platinum vrms”, which Fowler speculates stands for “voter record management system.”
The exposed databases were reported to a partner company of Platinum Technology Resource called Magenium. They were then restricted, but it is unknown how long the databases were exposed or who could have accessed them, with Fowler noting that “only an internal forensic audit could identify additional access or suspicious activity.”
Are you a pro? Subscribe to our newsletter
Sign up to the TechRadar Pro newsletter to get all the top news, opinion, features and guidance your business needs to succeed!
There were claims spread on social media during the 2020 election that votes were cast in the names of deceased family members, but Fowler cross-referenced several exposed death records and found that none of the deceased were listed on active voter databases.
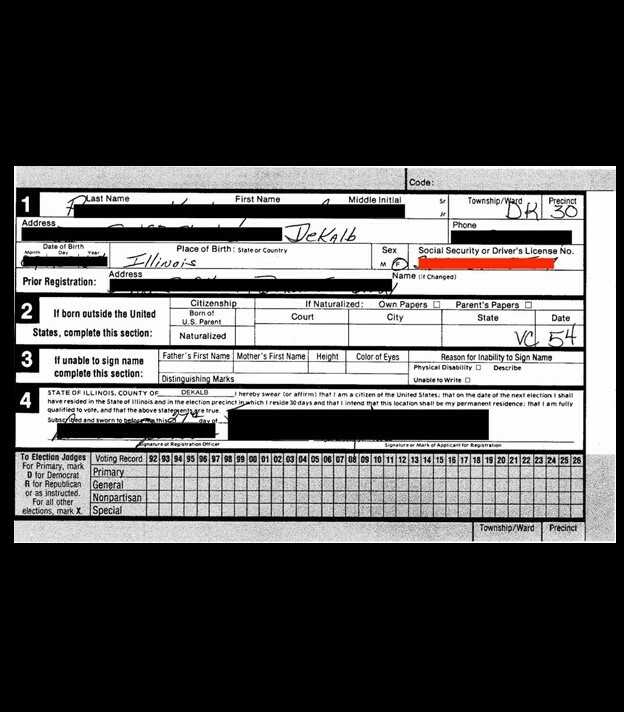
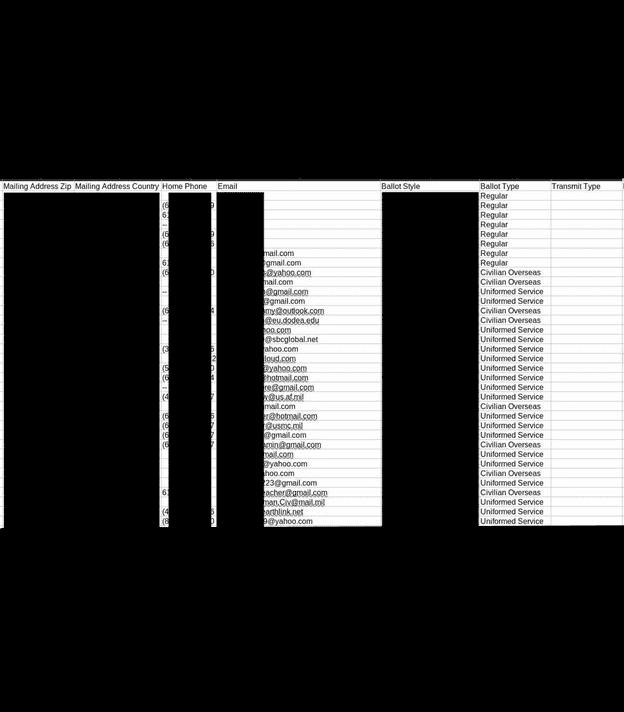
The other information exposed relating those on the active voter list could be used maliciously, as the information found within the databases included full names, physical address, some email addresses, date of birth, SSN (full and partial) or driver’s license number, and historical voting records. There were also copies of voter registration applications, death certificates, and records of change of address, jurisdiction, or state.
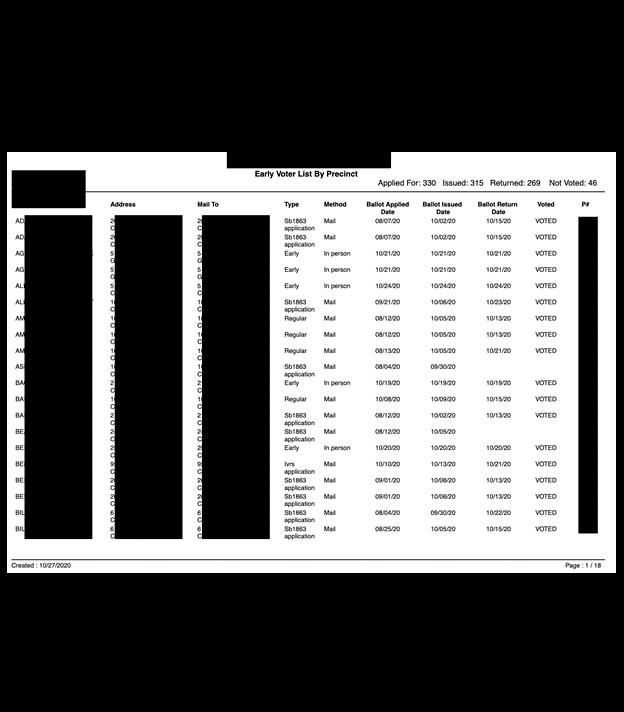
Additionally, candidate documents containing personal phone numbers, email addresses, and home addresses were identified, as well as petitions with voter signatures, addresses, candidate loyalty oath, economic interest, and additional supporting documentation. Fowler also uncovered documents marked as official ballot templates for primaries and general elections.
If these documents were accessed by nation states such as Russia or China, or by political activists, they could be used for mass disinformation campaigns or voter intimidation. There are also concerns that the information could be used by criminals to send out multiple ballots by mail in the name of one voter, sowing distrust in the electoral process and causing legal issues for the real voter whose name was used.
Fowler recommends that any organization that manages and stores sensitive information to follow cyber security best practices, alongside using unique formats for database names to prevent someone from jumping from one database to the next by simply replacing one word as Fowler did.
More from TechRadar Pro
- These are the best parental control apps around today
- US security services say DDoS attacks shouldn't affect elections this year
- Here are the best endpoint protection services

Benedict has been writing about security issues for over 7 years, first focusing on geopolitics and international relations while at the University of Buckingham. During this time he studied BA Politics with Journalism, for which he received a second-class honours (upper division), then continuing his studies at a postgraduate level, achieving a distinction in MA Security, Intelligence and Diplomacy. Upon joining TechRadar Pro as a Staff Writer, Benedict transitioned his focus towards cybersecurity, exploring state-sponsored threat actors, malware, social engineering, and national security. Benedict is also an expert on B2B security products, including firewalls, antivirus, endpoint security, and password management.