Is it safe to use AI website builders to create content?
AI content still needs human oversight
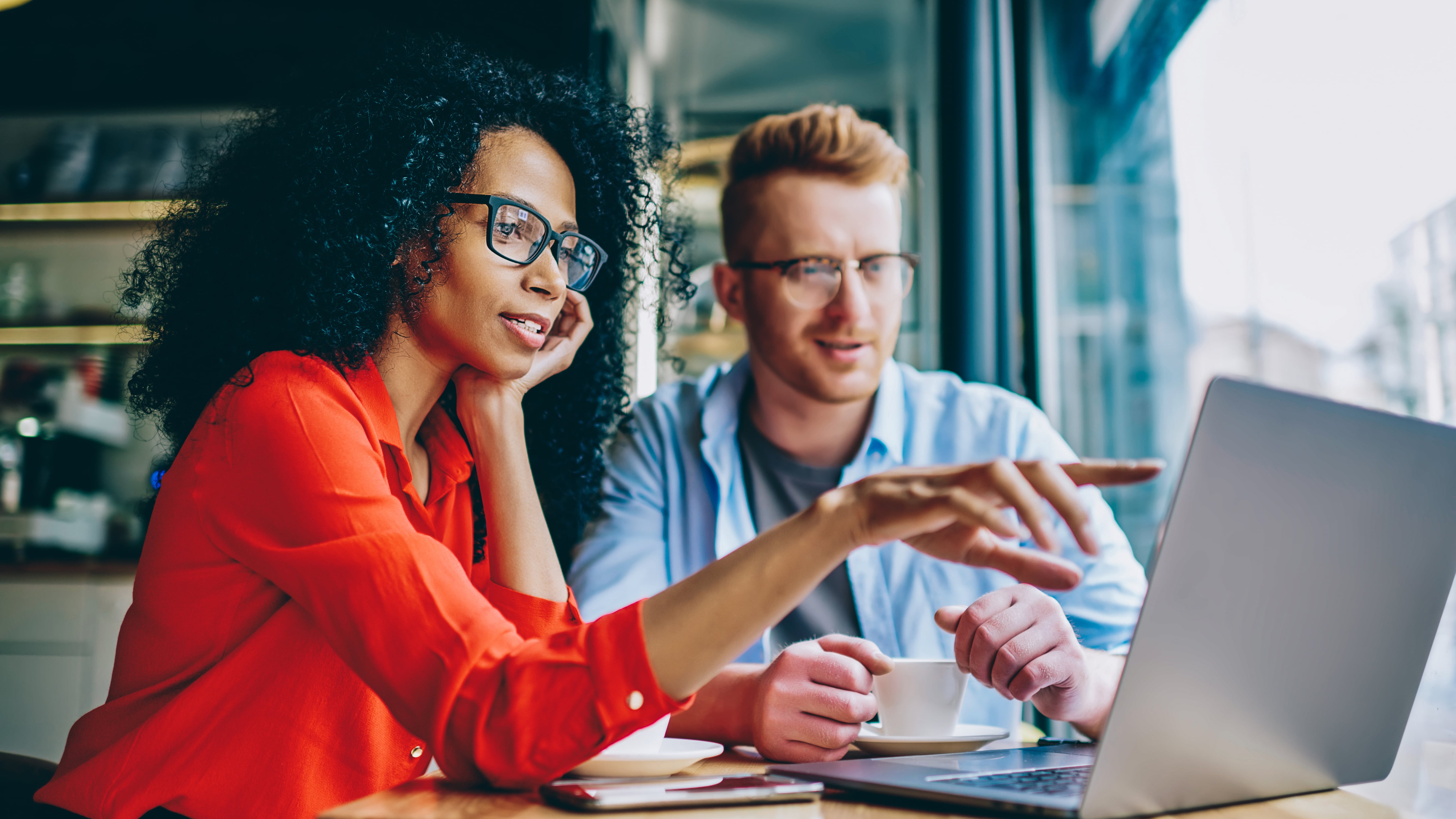

The best AI website builders promise to revolutionize the way we create online content. With just a few clicks and some simple inputs, these tools claim to generate professional-grade copy and visuals in minutes.
Sounds too good to be true, right? Well, you might be onto something.
While the best website builders can certainly streamline the website creation process by leveraging AI, the content they produce isn't always safe to use as-is. There are some hidden risks and limitations that you need to be aware of before hitting that "generate" button. In this article, we'll dive into the potential pitfalls of relying too heavily on AI to write your website copy and source your images.
How do AI builders generate website content?
Under the hood, AI website builders rely on sophisticated natural language processing (NLP) models to generate human-like text. These models, like the famous GPT-3 or Llama, are trained on massive amounts of online data, allowing them to learn the intricate patterns and relationships between words and sentences.
Here's a peek at how the process usually works:
- Training: First, the AI model goes through a rigorous training phase, consuming vast datasets of web pages, books, and articles to build its knowledge base.
- Input: When you're ready to generate some content, you provide the AI with a prompt or topic to guide the output. This could be a title, a few keywords, a tone, or a brief description of what you want.
- Generation: The model then works its magic, analyzing your input and using its training to predict and generate the most likely next words and sentences. It continues this process iteratively, constructing longer passages that mimic human-written content.
- Output: Once the model has generated a chunk of content, it spits out the result for you to review and edit.
- Iteration: If you're not quite satisfied with the output, you can ask the AI to take another pass, regenerate the content, or provide additional input to refine the results.
While the generated content can be impressively coherent and fluent, it's not perfect by any means. The AI model is ultimately just making educated guesses based on patterns in its training data. It doesn't truly understand the meaning behind the words it's stringing together.
Risks of using AI-generated copy
While the new AI-powered tools can generate website copy quickly and easily, there are several potential risks to be aware of. The generated text may contain factual inaccuracies, lack original ideas, or even unintentionally plagiarize existing content. Additionally, AI-generated copy often sounds generic and fails to capture a distinct brand voice.
Sign up to the TechRadar Pro newsletter to get all the top news, opinion, features and guidance your business needs to succeed!
Here are some of the key risks in more detail:
Factual inaccuracies
One of the biggest dangers of AI-generated content is that it can sometimes generate statements that sound plausible but are actually incorrect. The AI model isn't fact-checking or reasoning about the truth of what it's writing. It's simply predicting the most likely next word based on patterns it's seen before.
Plagiarism
Another risk to watch out for is accidental plagiarism. Remember, AI content generators are trained on existing web content. So, there's a chance that their outputs could closely resemble or even directly copy their source material, especially if your input prompt is very similar to the title or topic of an existing article.
Generic writing
AI language models are getting better every day at generating fluent, grammatically correct text. But one thing they still struggle with is originality and creativity. The content they produce often lacks the unique insights, personal anecdotes, and memorable turns of phrase that make human-written content so compelling.
Inconsistent branding
Speaking of brand personality, capturing and maintaining a distinctive brand voice is another challenge for AI models. They may generate copy that sounds incongruous with your company's established style, tone, and messaging.
Penalization
Finally, there's the risk of search engine penalization to consider. Major search engines like Google are constantly updating their algorithms to reward high-quality and original content that demonstrates real expertise and value for readers.
Dangers of using AI-produced visuals
Just like AI-generated text, visuals created by algorithms come with their own set of risks and limitations. While image generators can produce impressive and photorealistic visuals, they may contain biases, glitches, and artifacts that make them unsuitable for professional use. Using the AI-generated images without proper review can harm user trust.
Let's break down the dangers in more detail:
Copyright infringement
AI image generators are trained on datasets of millions of images scraped from the internet, including copyrighted photos and artwork. As a result, the visuals they generate can sometimes closely resemble or even directly copy the style and composition of existing works.
Lack of originality
Another downside of AI-generated visuals is that they often lack the creativity and originality of human-made art and photography. Because the AI models are essentially remixing and mimicking patterns and aesthetics from their training data, their outputs can feel generic, derivative, and forgettable.
Perpetuating biases
AI-generated visuals can perpetuate harmful biases present in their training data. Many of the image datasets used to train these models lack diverse representation and reflect societal biases around race, gender, age, and more.
Consent and privacy issues
With the rise of hyper-realistic AI image generation models like Stable Diffusion, it's now possible to create synthetic portraits of people who don't actually exist. While these AI-generated faces can be convenient placeholders, using them on your website and marketing materials raises some thorny ethical questions around consent and transparency.
Uncanny valley effect
One final risk to be aware of with AI-generated visuals is the dreaded "uncanny valley" effect. This refers to the unsettling feeling we get when an image looks almost, but not quite, real. Common issues include anatomical errors, mismatched lighting and shadows, illogical object placement, and garbled text.
Why human oversight matters in content creation
At the end of the day, while content generation tools can be incredibly powerful aids, they're not a complete substitute for human creativity and expertise. To create truly compelling, original, and trustworthy website content, you need to keep real humans in the loop.
Experienced writers, editors, designers, and subject matter experts play a vital role in ensuring the quality, accuracy, and impact of your published content. They bring invaluable skills to the table that AI simply can't match, like:
- Carefully fact-checking and editing AI-generated text to correct errors and add nuance
- Providing original analysis and insights that go beyond surface-level information
- Crafting content that aligns with your brand voice and resonates with your audience
- Identifying potential biases, inconsistencies, and ethical concerns in AI outputs
- Sourcing and creating bespoke, high-quality visuals that enhance your brand identity
In short, AI tools are best used as a complement to human expertise, not a replacement for it. By striking the right balance between AI efficiency and human creativity, you can unlock the full potential of these powerful technologies while still maintaining the authenticity and integrity of your content.

Ritoban Mukherjee is a tech and innovations journalist from West Bengal, India. These days, most of his work revolves around B2B software, such as AI website builders, VoIP platforms, and CRMs, among other things. He has also been published on Tom's Guide, Creative Bloq, IT Pro, Gizmodo, Quartz, and Mental Floss.
- Owain WilliamsB2B Editor, Website Builders & CRM