Google Chrome user profiles under attack from Emotet malware
Emotet has a new module that is targeting Chrome users
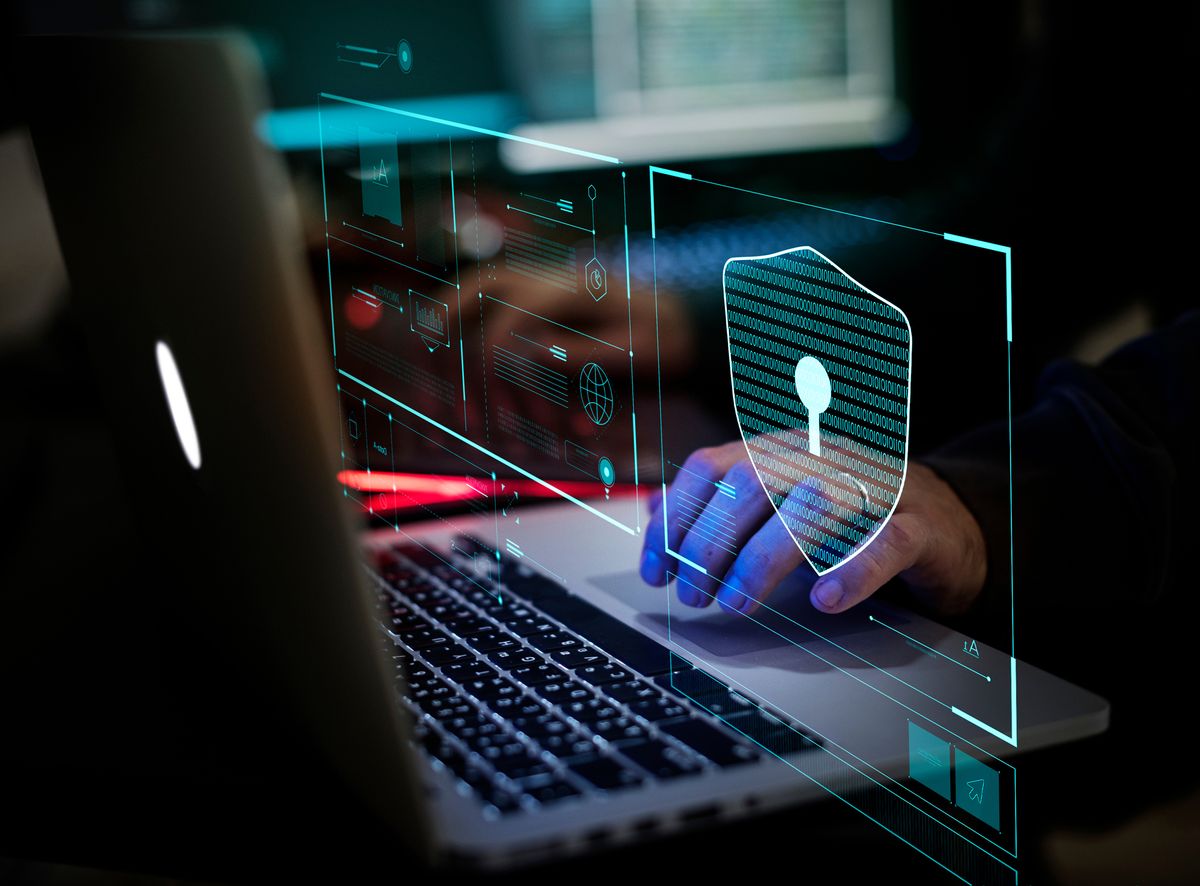

The Emotet botnet now has a brand new module that steals credit card information stored in Google Chrome user profiles.
Emotet was first spotted by cybersecurity researchers from Proofpoint dropping the new module on June 6. It tries to steal names, expiration dates, and card numbers stored in Chrome user profiles. An interesting detail is that the stealer exfiltrates the data to a command & control (C2) server that’s different from the module loader.
Emotet has had quite the ride. It was almost entirely wiped off the grid a year ago when German law enforcement used its own infrastructure to deliver a module that uninstalled the malware from all infected devices.
Share your thoughts on Cybersecurity and get a free copy of the Hacker's Manual 2022. Help us find how businesses are preparing for the post-Covid world and the implications of these activities on their cybersecurity plans. Enter your email at the end of this survey to get the bookazine, worth $10.99/£10.99.
Emotet is back
It returned half a year later in November 2021, when several cybersecurity researchers spotted Trickbot trying to download a DLL, identified as Emotet, to the system.
A little over a month ago, Emotet’s operators were spotted moving away from Microsoft Office macros for distribution, and towards Windows shortcut files (.lnk).
The malware was first seen in the wild back in 2014. At the time, it was used as a banking trojan, but has since evolved into a botnet. Some researchers believe it was developed by a threat actor known as Mummy Spider (AKA TA542) to serve as a dropper for second-stage viruses. Among others, Emotet was spotted dropping Qbot, and Trickbot which, in turn, were spotted delivering Cobalt Strike beacons, and various ransomware strains, including Ryuk, or Conti.
Today, it is able to steal sensitive and personally identifiable data, spy on traffic moving through compromised networks, and move laterally.
Are you a pro? Subscribe to our newsletter
Sign up to the TechRadar Pro newsletter to get all the top news, opinion, features and guidance your business needs to succeed!
Cybersecurity researchers from ESET recently said Emotet has had a significant increase in activity this year, "with its activity growing more than 100-fold vs T3 2021."
Via: BleepingComputer
Sead is a seasoned freelance journalist based in Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina. He writes about IT (cloud, IoT, 5G, VPN) and cybersecurity (ransomware, data breaches, laws and regulations). In his career, spanning more than a decade, he’s written for numerous media outlets, including Al Jazeera Balkans. He’s also held several modules on content writing for Represent Communications.